How can this SEO guide help my Business?

This SEO Guide will help you reach your target organic search audiences.
This SEO guide can improve your web page’s organic search position for top revenue generating keywords. The higher your pages appear in organic search for those keywords the more qualified traffic you get from in-market searchers needing your products or services. This translates into increased leads, sales and revenue.
With this guide you’ll learn step-by-step about key SEO factors that’ll boost your organic page rank, including:
- Keyword research: how to find the best audience targeted keywords for each page.
- How to combine keywords into phrases for incorporation into page content.
- How to write META tags: learn how to write eye-catching, compelling META Titles and Descriptions (your search result has less than one second to get the attention of in-market searchers!).
- Image alt-tags: keyword rich descriptions of images.
- Headings: each section of a page should be divided into sub-sections with keyword rich headings.
- XML sitemaps: get your product and service pages indexed on search engines with XML sitemaps.
What are the Goals of an SEO Guide?
- A short step-by-step guide on SEO for startups and small business web sites.
- Make changes to your website to improve your visibility in Google and Bing.
- Find the top keywords that have lots of traffic for your topic.
- How to add those keywords to your page.
- Your audience can find your page in Google.
How to do SEO Keyword Research
Find the Keywords
The first step is to find keywords that are both relevant and have lots of traffic. We will do this by using several tools and steps. At the end, we will have one spreadsheet with seven or eight worksheets. One of the worksheets will be the final collection of top keywords.
How can Google Ads Help with Keyword Research?
There are several research options to develop a keyword list in Google Ads. We recommend using both to compare results, the first (Discover new keywords), and then the second (Get search volume and forecasts).
1. Discover new keywords
Open Google Ads | Tools | Keyword Planner and select “Discover new keywords”.
(see Figure 1 below)
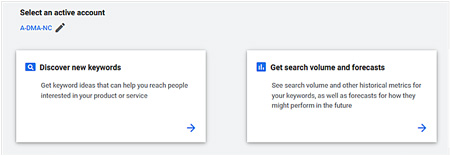
Figure 1: Select “Discover new keywords”
- Select if you want to start with seed keywords (Start with Keywords) or a website address (Start with a Website— see Figure 2 below).
- Set the location and language. If you are interested in keywords for France, set the Targeting to France. Set Languages to French. If you’re interested only in Canada, don’t set the location to “All Locations”. That will include data for South America, Africa, and so on, which will mess up your data (see Figure 2 below).
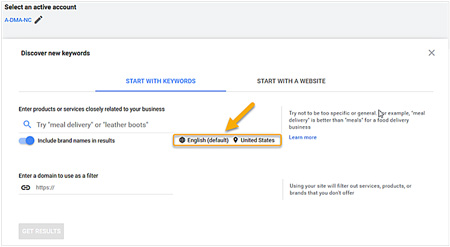
Figure 2: Important: Select your default language and country.
- If you use Start with Keywords: add up to 10 keywords and use a domain (website) address (either yours or a competitor’s).
- If you use Start with a Website: enter your website address or a competitor’s. Select the entire website, or a specific page to research one product or service.
Click “Get Results” - Set the Date Range to the last four years to get the most data (see Figure 3 below).
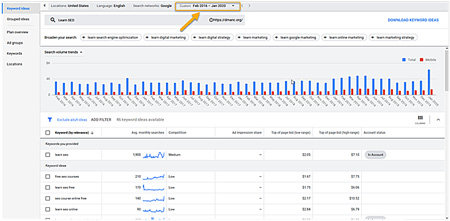
Figure 3: Set your “Date Range” to at least 4 years back.
- Click Download Keyword Ideas in the top Left corner to get your keywords.
- Add each spreadsheet of keywords to a main spreadsheet.
2. Get search volume and forecasts
Once you’ve developed a list of keywords from “Discover new keywords” you can “See search volume and other historical metrics for your keywords, as well as forecasts for how they might perform in the future.” (Google Keyword Planner)
- Click on “Get search volume and forecasts” (see Figure 4 below).
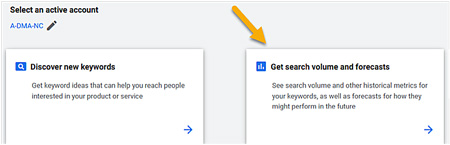
Figure 4: Check search volume and forecasts for your keywords.
- Copy and paste your keywords from “Discover new keywords” and any other lists into the box or upload your keyword list file (see Figure 5 below).
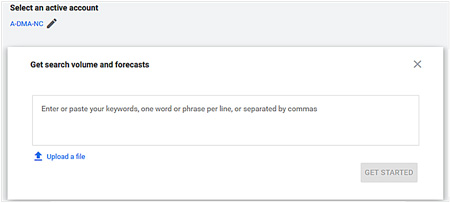
Figure 5: Copy and paste or upload a file with your keywords here. Then click “Get Started”.
Click “Get Started”
In the next screen you will see forecasts of how your keywords within a campaign will perform, negative keywords and historical metrics (a dash “-“ means there’s not enough data) (see Figure 6 below).
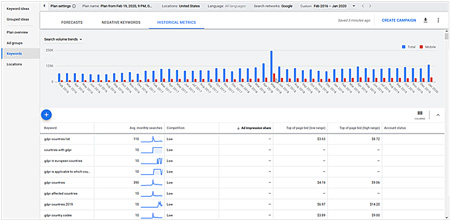
Figure 6: Performance forecasts, negative keywords and historical metrics for your keyword list.
Competitor Research with Google Ads
Instead of keywords and your company’s URL, you can insert your competitors’ URL into the Google Ads Keyword Planner tool. This shows what Google thinks your competitor’s website is about.
- Make a list of five similar competitors. They should be in your market and generally about the same size as your company.
- Go to Google Ads | Tools & Settings | Keyword Planner (see Figure 7 below).

Figure 7: Use Keyword Planner to check your competitor’s keywords.
- Repeat steps 1 (Discover new keywords) and 2 (Get search volume and forecasts) from above for your five competitor’s websites.
- Copy the five spreadsheets into your main spreadsheet. Copy each spreadsheet and paste it as a worksheet. Name the worksheets Competitor-1, Competitor-2, Competitor-3, and so on. Use the names of your competitors.
- If a website is new or Google’s computer doesn’t understand it, there may not be keywords for it or Google shows wrong keywords.
- You should check your own website. If the displayed keywords are relevant, then you’ve done a good job. But if Google shows irrelevant keywords or very few keywords, then your site’s content is unclear.
More Keyword Research with Google Ads
Google Ads has another tool to show keywords: the Search Terms report (see Figure 8 below).
- Set the calendar to All Time.
- Select Keywords | Search Terms.
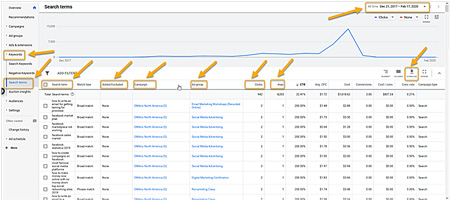
Figure 8: Use the Search Terms Report to find additional keywords.
- This shows you a table of keywords that brought traffic to your site. This includes keywords in your Google Ads account. It also includes keywords that are not in your Google Ads account.
- Click the down arrow to download the table as a spreadsheet : to the upper right, just above the table (see Figure 8 above).
- Keep the following columns: Search Term, Added/Excluded, Campaign, Ad Group, Clicks, Impressions. You may delete the other columns.
- Sort the list by impressions.
- Copy this spreadsheet into your main spreadsheet.
How can Google Analytics be used for SEO Keyword Research?
Still here? Okay, next tool. Let’s use Google Analytics to get more keywords. This shows more keywords that people use to reach your site. For this to work, you must first install Google Search Console and tie it to your analytics Account. View the following links to set up Google Analytics, Google Search Console (GSC) and how to add GSC to Google Analytics. (note: Google Analytics will fully incorporate GSC, but until then these instructions are necessary.)
Setting up Google Analytics:
https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/1008015?hl=en
Setting up Google Search Console (GSC):
https://support.google.com/webmasters/answer/34592?hl=en
Adding GSC to Google Analytics:
https://support.google.com/analytics/answer/1308621?hl=en
- Open Google Analytics | Acquisition | Search Console | Queries.
- Sort by clicks (click the heading “Clicks”).
- You’ll notice that the top keyword is “(not set)”. For no real reason, Google won’t show you a bunch of keywords for your site. But you get these from other tools, don’t you? So, what’s the point for Google to not show these? Whatever.
- At the right-bottom of the screen, it shows that you are viewing the first 10 rows of 2,000 rows. Set this to show as many rows as possible.
- Download the spreadsheet. Keep the columns “Search Query, Clicks, Impressions”. You can delete the rest.
- Add this as a worksheet to your main spreadsheet.
Note: Look at the top 10-30 keywords. You may think your website is one thing but most visitors come to your site for an entirely different topic. You may want to expand the top pages or add additional pages based on those keywords. Write metatags for those pages that include the search terms that people are using.
Level of Indexation
While we’re in Google Search Console, let’s look at the Index Coverage report. This tells us how many pages of your website have been indexed by Google.
- Go to Google Search Console | Index | Coverage (see Figure 9 below).
- At the top, the Index Coverage report shows “All known pages”. These are the pages Google has found on your site. They are broken down into four categories:
- Error: “These are pages that couldn’t be indexed for some reason.”
- Valid with warning: “These are pages that have been indexed, but there are some issues, and we’re not sure if they are intentional on your part.”
- Valid: “These pages have been indexed.”
- Excluded: “These are pages that were intentionally not indexed.”
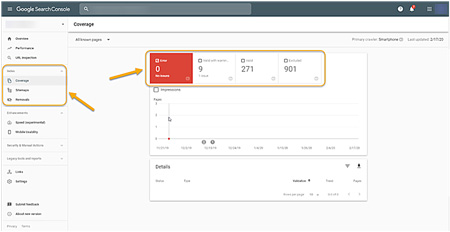
Figure 9: Use Google Search Console to make certain your pages are indexed in Google.
- Compare the Valid number with the number of pages on your site. If you have 70 pages, then 60 / 70 = .857 X 100 = 85.7%. This means 86% of your site has been indexed, and are considered valid by Google.
- I’ve often seen indexation levels at 15% or 20%. That’s pretty bad; most of the website is unfindable. You should have 95% or greater indexation.
- To get high indexation, create an XML site map, image site map, mobile site map and news site map. Wait a few days and check your indexation again.
- Of course, nothing with Google is this easy. Just because your webpage is in Google’s database doesn’t mean your page will be found. You have to be in the database, and you need to have traffic to the page.
- If the page doesn’t have traffic, the page is spammy (you use too many keywords and so on), or the page has errors that need to be corrected, or the page has duplicate content (80% or more of the text is a copy of other pages), then your page will be in Google’s index, but Google will lower its ranking so much that nobody will see it.
Final Step: Combine the Worksheets
By now, you have ten or fifteen worksheets in your spreadsheet.
- Create a new worksheet and name it “Top-Keywords”.
- Copy all of the worksheets into the Top-Keywords worksheet. You may end up with several thousand keywords.
- You now have a list of all of the keywords for your industry/market.
- You only need the columns Keyword and Average Monthly Searches.
- If there are keywords without data for Average Monthly Searches, make a copy of those and use Google Ads | Tools & Settings | Keyword Planner | Get search volume and forecasts to get search volume data.
- Sort the list by “Avg. Monthly Searches”.
- You only need to look at the keywords with lots of monthly searches.
- Go through the list and pick out the keywords that are relevant to your project.
- Combine Keywords in Phrases.
Look for keywords that can be combined into a phrase. For example, you have keywords such as “best charity” and “donate money”. You can combine these into one phrase (“donate money to the best charity”) which covers both keywords. Combine as many keywords as you can.
Which Pages for SEO?
If you have 10-15 pages, you can do the SEO work in a few days. But if you have 50,000 pages (or 1.5m pages…), that’s too much. And there’s no point in doing all of those pages. Some SEO companies will offer to fix all 50,000 pages, but that’s a waste of your money. There’s no point doing SEO work on pages that don’t appear in search engines. Do SEO only on pages which bring new users. How to find those?
- Go to Google Search Console | Performance | Pages tab. Check yes for all of the boxes (Clicks, Impressions, Position). Select the Pages tab. Set the date range as far back as possible (see Figure 10 below).
- The graph shows your website’s pages in Google. These are the pages that people see in Google. Download the list (click the down arrow icon).
- Now go to Google Analytics | Behavior | Site Content | Landing Pages.
- Sort the table by New Users. These are the pages where new users come to your site. Download this table.
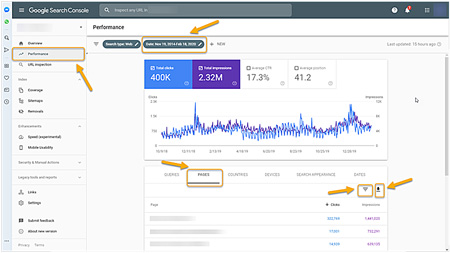
Figure 10: Also use Google Search Console to determine which pages to SEO.
- Combine both of these tables.
- Look for pages with lots of impressions, lots of clicks, and high ranking (position 1, 2, or 3). Make a list of those pages.
- Do very good SEO work on these pages.
- Go to Google Ads | Tools | Keyword Planner.
- Instead of pasting keywords into the first box (“Search for New Keywords Using a Phrase, Website, or Category”), paste your competitor’s URL in the box “Your Landing Page”.
- Copy the five spreadsheets into your main spreadsheet. Copy each spreadsheet and paste it as a worksheet. Name the worksheets Competitor-1, Competitor-2, Competitor-3, and so on. Use the names of your competitors.
- If a website is new or Google’s computer doesn’t understand it, there may not be keywords for it or Google shows wrong keywords.
- You should check your own website. If the displayed keywords are relevant, then you’ve done a good job. But if Google shows irrelevant keywords or very few keywords, then your site’s content is unclear.
How do I Use Keywords in Meta-Tags?
Before we take the next step of reviewing competitors’ meta-tags, we have to make a new worksheet.
- Make a worksheet for your meta-tags and name it “Meta-tags” (see Figure 11 below).
- Create the following columns: URL, Name, Keyword, TITLE, Chars, DESCRIPTION, Chars, and Heading. The column “Name” is for the name of the page. The column “Keyword” is for the top keyword for the page.
- The Chars columns are special columns: they tell you how many characters you have for the TITLE and DESCRIPTION tags. You can only have 68 characters (including spaces) in the TITLE tag, so it’s useful to know the number.
- To use this, click in the cell and enter the formula “=SUM((LEN(D2)))” (without citation marks). Where it has D2, enter the TITLE cell’s information (column and row).
- For example, D2 is column d, row 2. Type a few words into the cell for TITLE (where it says “Official Site” below).
- If you did this right, the Char cell will show the number of characters (13) in the TITLE cell.
Here’s an example of the meta-tags worksheet:
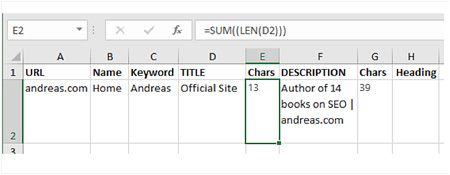
Figure 11: Create a Meta-tags spreadsheet.
- At the top center of the screen shot, you can see the formula for cell E2. It shows the number of characters in the cell D2. Cell G2 uses the same formula to count the characters in cell F2.
How Can I Research My Competitors’ Meta-Tags?
- Open the worksheet named “Meta-tags”.
- Open your competitor’s website in a browser.
- Right-click and select View Source to see the HTML code.
- Use Ctrl-F (find), search for TITLE, and copy the title tag.
- Use Ctrl-F (find), search for DESC, and copy the description tag.
- Do this for five to ten of your competitors.
- You can know how your competitors are doing SEO. If the DESCRIPTION tag is blank or the TITLE tag and DESCRIPTION tag are poorly written, then they’re not trying. Very likely, they have low traffic. That’s good news for you.
How do I Write the TITLE Tag?
- Write a TITLE tag that encourages visitors to come to your webpage. The TITLE tag states the benefits to your visitors. Use the keyword first and then the name of the webpage.
- Google allows around 68 characters (including spaces) in the TITLE tag. Sometimes, it’s more and sometimes, it’s less.
- The TITLE tag should open with the top keyword, state the URL, and add a city or telephone if relevant.
- Use the pattern.
- For example, <TITLE>San Francisco Crab Dinner | Franciscan.com | Pier 43 | 415.362.7733</TITLE>.
How do I Write the DESCRIPTION Tag?
- Use your top two or three keywords to write several phrases.
- Use up to 180 characters (including spaces) in the DESCRIPTION tag.
- Use the pattern.
- For example, <META name=”description” content=”San Francisco seafood at its best! Fresh crab, lobster, oysters, salmon, sea bass, filet mignon, short ribs, and more!
Tel. 415.362.7733. Call Now!”>. - Open with the top keywords, describe the benefit for the visitor, and close with CTA (call to action), such as “Call Now, Visit Us, Buy Now”.
- Use lots of the keywords that your audience wants to see.
How do I Write the KEYWORD Tag?
Google, Bing, and Yandex ignore the meta-KEYWORD tag. You don’t need to use this.
Here’s an example: <meta name=”KEYWORD” content=”goldfish, backyard pond, frog pond”>.
You can either put a few keywords there to fill the space or just not use it. It doesn’t matter.
How do I Write ALT Tags in the Images?
The image link has an ALT tag that holds text about the image. You can use this to add a sentence of descriptive text.
- Here’s an example: <img src=”images/goldfish.gif” ALT=”Get goldfish for your pond at Goldfish.com. Los Angeles. Tel. 555.123.4567”>.
- The amount of text should be proportionate to the size of the image. If the image is a small button, don’t add a long paragraph of text.
How do I Write the Page Heading?
Search engines pay attention to a page heading because it has information about the page.
- The heading should use the H1 tag (H1 = heading).
- Use your top keywords as the first two or three words in the heading.
- Here’s an example of an H1 tag:
<h1>How to Pick Goldfish for Your Pond</h1>. - The most common problem with headings is use of the wrong tag. Many web designers don’t like the H1 heading because it uses a big font. They choose instead images, SPAN tags, or DIV tags.
- That looks nice, but search engines can’t tell if those images are headings. Body text that uses SPAN will be treated as body text, not as header text. You must use H1 formatting. You can still have your design. Use CSS to modify the look of the H1 tag so it renders the way you want it.
How do I Write the Text on the Page?
The text on the page should be descriptive, informational, and include the main keywords.
- Use your keywords in the first two to three words of the body text.
- Use the tag to mark body text.
- Write naturally. Don’t stuff keywords into a page. Don’t use keyword-density tools. Search engines have tools to detect machine-generated text.
TIP: Don’t open the first paragraph with a sentence that starts with a clause, such as “If you are looking for something nice to put in your pond….” People scan the first few words of the first paragraph. If it’s not relevant, they go back to the search engine. Open the first sentence with your keywords. For example, “Goldfish are the ideal fish for your backyard pond.”
A Few More Tips
How can I Make an XML Sitemap?
- An XML sitemap is a list of all pages at your website. Submit it to Google and it’ll index your entire site.
- Make an XML sitemap of your site with XML-Sitemaps.com.
- Download it to your computer, upload to your server, and submit to Google Search Console.
Why Should I Post My Company’s URL to Twitter?
- To quickly get in Google, tweet your URL in Twitter. Write a short description of the page and add the URL.
How can I Test TITLE and DESCRIPTION Tags?
- You can use Google Ads to test TITLE tags. Create ads with different TITLE tags, show them until you have more than 1,000 impressions for each one, and select the one with the highest click-through rate (CTR).
- You can also test TITLE tags in Google Analytics. In Google Analytics, go to Behavior | Site Content | All Pages, then change the Secondary Dimension to Page Title. The report shows the page’s traffic. Use keywords to write different TITLE tags and see if the traffic improves.
More about SEO
GOOD NEWS: Basic SEO gets you into Google and people may be able to find your site.
BAD NEWS: Google is much more complicated than this.
BETTER NEWS: Most of your competitors are really bad at SEO. So if you do just an okay job, you’ll be ahead of them. If you learn more SEO and do a great job, you’ll be at the top of the search results.
- There is also SEO for YouTube, apps, social media, and mobile.
- We’ve provided this guide to give you an idea of the steps needed to do good SEO. It is a time-consuming project, and there are many technical factors which can affect whether Google can index your website.
Author: Andreas Ramos
Vice President, Digital Marketing
Beasley Direct and Online Marketing, Inc.
For help with your SEO project, contact us at BeasleyDirect.com. We’ve worked on dozens and dozens of SEO audits and improved organic search results 20-50% for our SEO clients.



